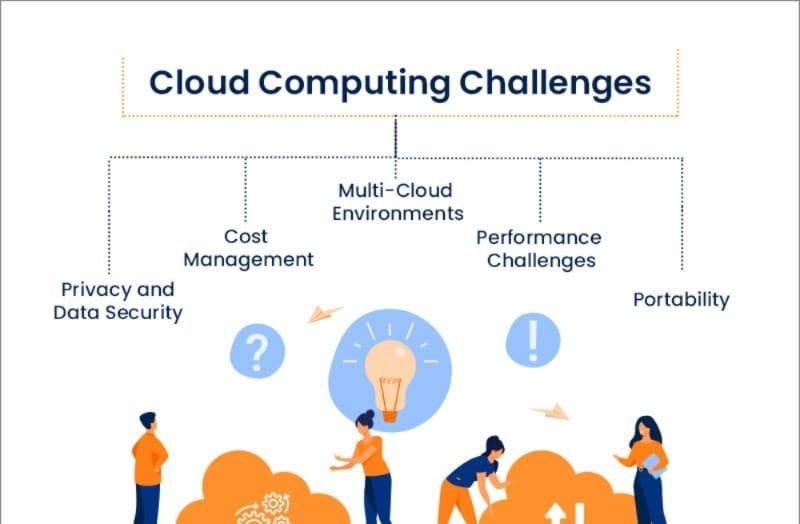
Data Science and AI’s Increasing Role in Telecom
In today’s world, telecom is becoming more and more digital. Voice conversations are transmitted digitally, data services are frequently more important and profitable than voice services, and more and more of the industry’s infrastructure is digital and software-driven every year. Additionally, the customer service and back-office processes of the telecom sector are experiencing digital transformation.
AI and data science are essential to the sector and will only become more so as it develops. Massive volumes of data are produced by telecom firms’ infrastructure, network, and customer service operations. Data science is now so widely used in telecom because of this. Data science and AI in telecom give operators the capabilities to analyse the data and apply it for a variety of purposes, including boosting dependability, cutting costs, and enhancing customer service.
Demand for AI and Data Science in Telecom
The need for data scientists is only growing as a result of the enormous amount of data that the telecom sector generates. According to Analytics Insight research, the telecoms and IT sector holds a 33 percent market share and is driving the explosive increase in big data. The association estimates that spending on big data in telecom would increase from $59 billion in 2019 to over $105 billion in 2023, putting that into context. By 2023, there will be over four million employment openings in the field, increasing demand for qualified workers.
The Demand for Data Science and AI in Telecom is Being Driven by COVID-19
The COVID-19 epidemic has accelerated the demand for data science in telecom, which has been driven in recent years by the Internet of Things (IoT), the development of 5G, and growing customer appetite for individualised offerings. Almost every sector that relies on digital communications, including schools, healthcare and pharma, government organisations, and the global supply chain, now more than ever recognises the necessity of dependable connectivity. The telecom industry is increasingly embracing data science, AI, and automation to ensure that crucial communications in this new remote world remain smooth during the crisis, despite fewer workforce and limited access to infrastructure like contact centres and data centres.
How Businesses Can Use AI and Data Science in Telecom
There is no restriction on how telecom companies can use data science and AI in their various industries, but here are some examples of current implementations.
Network Security
Cybercriminals find telecommunications to be a very alluring target. After all, they connect to almost everything in the modern digital world through intricate, international networks. They also keep a tonne of very private data in storage. Companies can use data science to view events in real-time, spot security abnormalities, and do predictive analysis to understand where vulnerabilities are and how to proactively mitigate them. Additionally, businesses can examine threat trends to stop them before they spread too widely by utilising machine learning in the telecom industry.
Mitigation of Fraud
Customers who use telecom networks are also susceptible to cybercrime. Additionally, the epidemic is making things worse. The cost of fraud to the global telecom business was estimated at a staggering $29 billion in 2018, according to a study by the Communications Fraud Control Association (CFCA). Fraud is so pervasive in the telecom sector. Big data in telecom allows businesses to analyse real-time data to pinpoint the origin of fraudulent transactions and link them to earlier activities to stop further counterfeiting.
Optimal Network Design
More people are depending on network access, particularly during COVID-19 outages, thus telecommunications must make sure that speed and performance are always at their best. They are utilising data science, AI, and machine learning algorithms to find patterns in data that help them discover and predict abnormalities before customers suffer any service degradation in order to do this.
The Client Experience
Personalization and prompt resolution of any concerns clients may be having are two crucial components of this. Based on their previous contacts and preferences, telecoms use data science, AI, and analytics to ascertain what clients want. Through logical self-service menus, chatbots, and natural language processing (NLP) made possible by machine learning, telecoms also use AI to offer quick and intelligent customer service.
Automated Robotic Process (RPA)
RPA is widely used in the telecom industry to automate repetitive procedures, which reduces errors, saves labour and expenses, and speeds up operations. There are various ways RPA might help telecom organisations, according to CustomerThink, a global online community of business and thought leaders that routinely comments on customer-centric strategy.